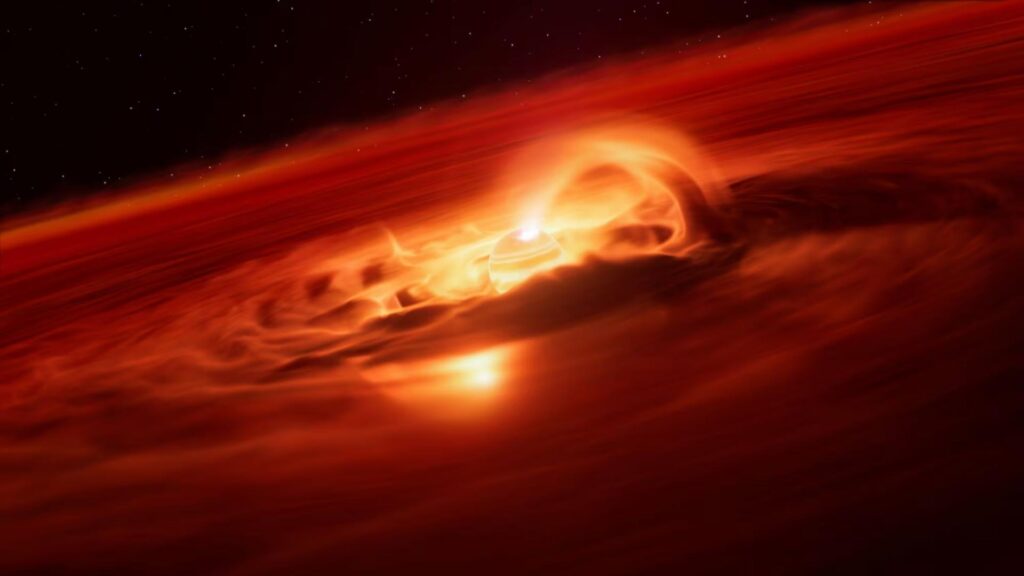
Astronomers have observed a planet that in some ways behaves more like a star — including a massive growth spurt unlike anything witnessed before in a free-floating planet.
The rogue planet, which does not orbit any star, is called Cha 1107-7626 and is outside of our solar system, 620 light-years from Earth in the Chamaeleon constellation. A single light-year, or the distance light travels in one year, is equal to 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers).
The planet has a mass five to 10 times that of Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system. And it’s getting bigger every second, according to new research published Thursday in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
ESO/L. Calçada, M. Kornmesser
Astronomers have observed a planet that in some ways behaves more like a star — including a massive growth spurt unlike anything witnessed before in a free-floating planet.
The rogue planet, which does not orbit any star, is called Cha 1107-7626 and is outside of our solar system, 620 light-years from Earth in the Chamaeleon constellation. A single light-year, or the distance light travels in one year, is equal to 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers).
The planet has a mass five to 10 times that of Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system. And it’s getting bigger every second, according to new research published Thursday in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Estimated to be 1 million to 2 million years old, Cha 1107-7626 is still forming, said study coauthor Aleks Scholz, an astronomer at the University of St. Andrews in Scotland. It may sound old, but astronomically speaking, the planet is in its infancy. By contrast, the planets in our solar system are about 4.5 billion years old.

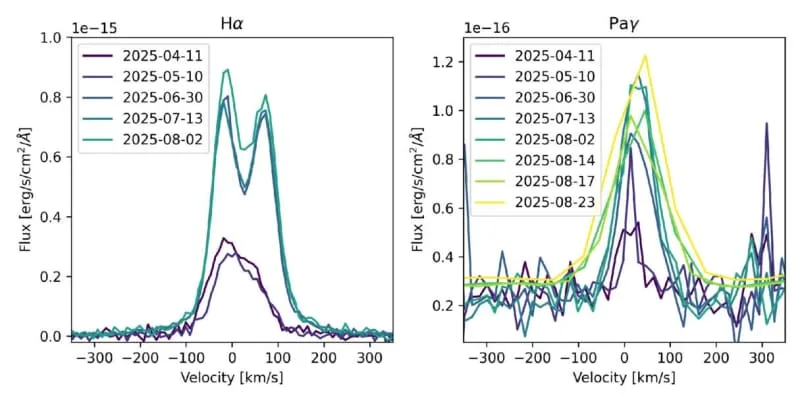
Cha 1107-7626 is surrounded by a disk of gas and dust, which constantly falls onto the planet and accumulates during a process that astronomers call accretion. But the rate at which the young planet is growing varies, the study authors said.
Observations with the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in Chile’s Atacama Desert, along with follow-up views conducted by the James Webb Space Telescope, showed that the planet is adding material about eight times faster than a few months earlier and gobbling up gas and dust at a record rate of 6.6 billion tons (6 billion metric tons) per second.



